If you are relatively new to electrical engineering as a discipline, you have likely encountered a number of basic components and their fundamental operation. But there are some more bespoke component types, the properties of which are taken for granted by the average consumer. One of these is the piezo buzzer – but how does it work?
What is a Piezo Buzzer?
Buzzers are a form of electronic device, that emit a sound when they receive an electrical signal. They have a wide variety of applications, with different kinds of buzzer more suited to different purposes. Of these different kinds of buzzer, the piezoelectric buzzer – otherwise known as the piezo buzzer – is one of the most common.
Piezoelectricity is a fundamental process in modern electronics, that describes the unique ability of certain crystalline materials to convert pressure or movement into electrical energy. This principle is used in the form of transducer or ‘contact’ microphones, where a sound signal vibrates a surface and the piezo pickup translates said vibrations into electrical information. The inverse is also possible, where the material receives an electric signal and converts it into mechanical and heat energy.
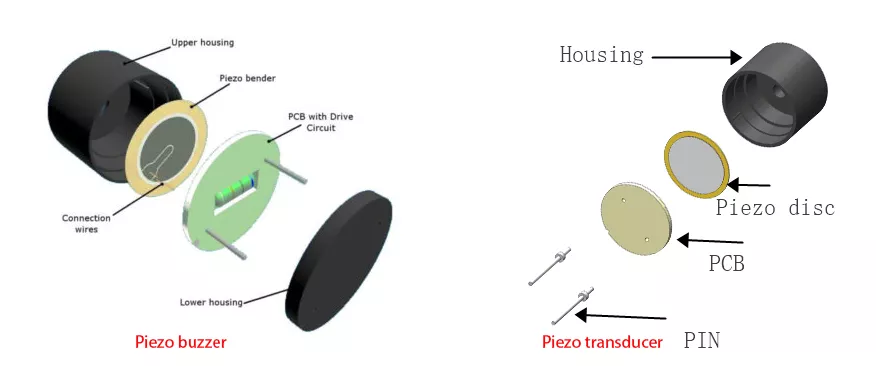
A piezo buzzer consists of a piezoceramic material encased in a small enclosure, with two solder tags or loops for the positive and negative terminals of the material. A voltage is applied to the buzzer, and the material translates that voltage into its corresponding sound or tone by applying pressure to the air around it.
Applications for Piezo Buzzers
Piezo buzzers are used in a wide variety of tools, devices and circuits, with a number of different variants and sizes producing different results. In industrial and commercial settings, piezo buzzers are commonly used in alarms or alert systems to deliver warning tones.
They are also commonly used in disposable electrical items and low-cost toys, as a method of delivery for sound effects and audio information. One commonly-encountered example is in the ‘singing birthday card’, that delivers a tune when opened.
Piezo buzzers are limited in their scope, though. While they do see regular use as an inexpensive alternative to a speaker cone in small toys and gadget, the frequency response of the piezoceramic material renders it ineffective at delivering high-quality audio information. However, it is able to translate sounds to high-quality electrical signals in its inverse function as a pickup or microphone.
Piezo Vs Magnetic Buzzer
Piezoelectricity is not the only process by which buzzers are made possible. There are other kinds of buzzer that utilize different principles to create sound. For example, magnetic buzzers use an electromagnetic coil to flex a magnetic disc in time with the fluctuations in the field it creates – producing an audible tone.
The key difference is in the operating voltages and relative size of the two types of buzzers. Piezo buzzers are smaller and can operate at higher voltages, but magnetic buzzers can be louder and more power-hungry.