Sheet metal fabrication involves cutting, bending, and assembling metal to create various items. Its applications range from car parts to medical devices. The technique begins with design and planning. It then moves through different stages, each critical to the final product. The fabrication methods vary based on material, thickness, and project complexity.
Let’s explore the key aspects of the sheet metal fabrication process, shedding light on its intricacies and importance.
What is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Before discussing the sheet metal fabrication process in detail, What is Sheet metal fabrication? It is a comprehensive process that involves shaping and molding metal into finished products or parts. This process is foundational in manufacturing, catering to automotive, aerospace, energy, oil& gas, and many more industries.

Its versatility allows for diverse and complex shapes across various applications. This process supports innovation by enabling custom designs and rapid prototyping. Moreover, fabrication techniques like cutting, bending, and welding contribute to the durability and functionality of the final products.
Moreover, China Sheet Metal Fabrication has become synonymous with cost-effectiveness in the global context. It is known for its competitive pricing due to labor costs, technological innovation, and advanced industrial infrastructure. All these reasons have made China a go-to destination for businesses looking to reduce fabrication costs without compromising quality
Cutting Techniques in Sheet Metal Fabrication
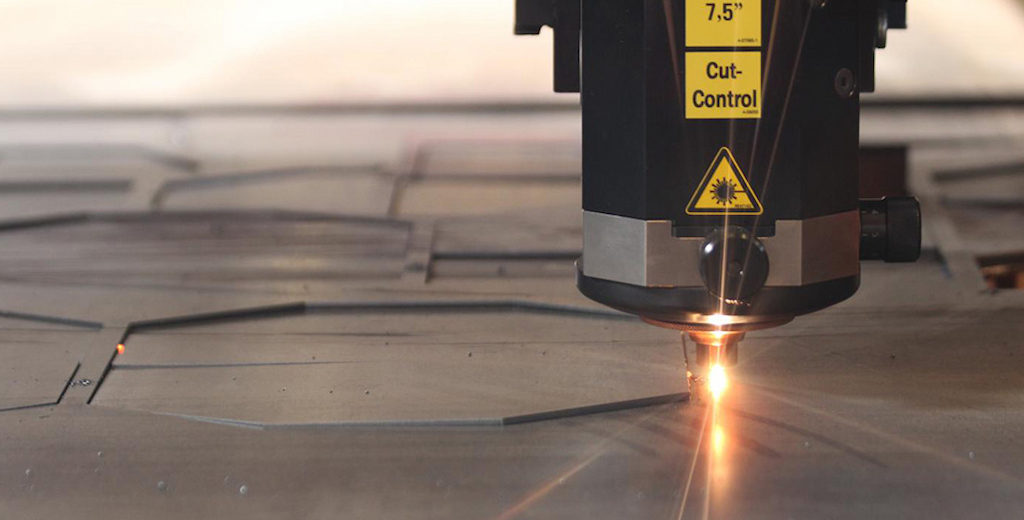
Laser cutting process
Cutting is the foundational step in sheet metal fabrication, dictating the shape and size of the final product. The precision and quality of cutting heavily influence the overall quality of the fabricated item. There are several cutting techniques, each with unique advantages and suited for different material types and design requirements. These methods range from traditional mechanical cutting to advanced laser and waterjet cutting, offering diverse capabilities to meet diverse fabrication needs.
- Laser Cutting – Precision and Versatility: Utilizes a concentrated laser beam for high precision, ideal for intricate designs.
- Waterjet Cutting – For Intricate Designs: Employs a high-pressure water stream, perfect for heat-sensitive materials, preserving integrity.
Bending and Forming in Fabrication
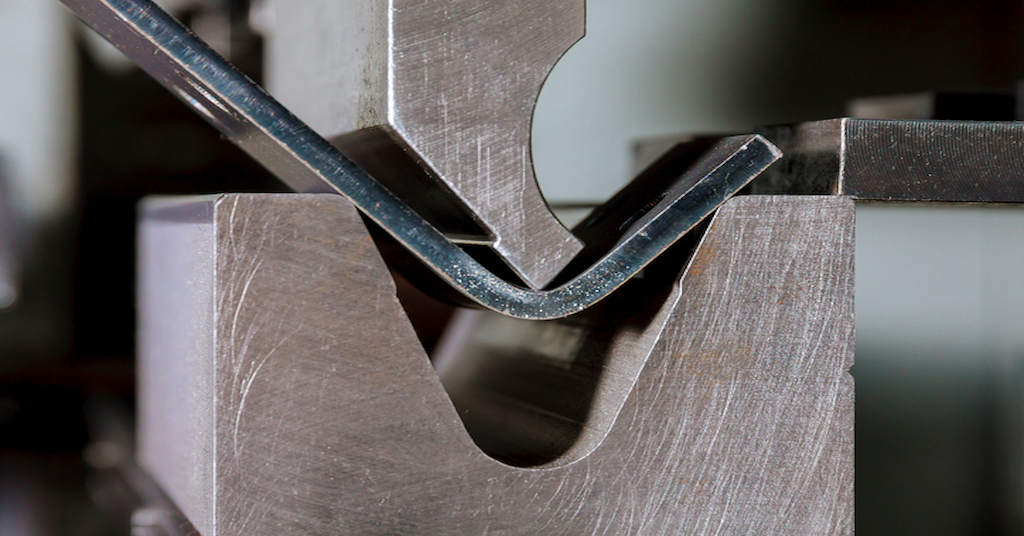

Sheet metal bending
After cutting, the metal sheets undergo bending and forming, crucial steps that transform flat sheets into three-dimensional shapes. This stage is vital for creating the structural aspects of the component, and the technique chosen depends on the specific requirements of the bend, such as the angle, radius, and metal type.
- Press Brake Forming for Accurate Bends: Provides precise bends with a press brake machine, suitable for several angles.
- Roll Bending for Curves and Circles: Ideal for creating smooth curves and circles, using a series of rollers for gradual shaping.
Joining Techniques in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Joining is the next crucial phase in sheet metal fabrication, where the cut and formed pieces are combined to create a cohesive structure. The method of joining depends on the strength requirements, the type of materials used, and the intended application of the final product. Proper joining is essential for the structural integrity and functionality of the fabricated item.
| Technique | Description |
| Welding | Ensuring Strong Joints: A common and robust method for joining metal pieces, suitable for many applications. |
| Riveting | An Alternative to Welding: Provides a less invasive option than welding, ideal for delicate or thin materials. |
| Soldering | Joining Smaller Parts: Utilizes molten metal to join smaller components, ideal for electronics and precision assemblies. |
| Brazing | High-Strength Joining: Uses a filler metal with a higher melting point than soldering but lower than the base materials, for strong, temperature-resistant joints. |
| Adhesive Bonding | Bonding Without Heat: Employs adhesives to join materials, suitable for combining dissimilar materials and sensitive components. |
| Mechanical Fastening | Utilizes mechanical means such as screws, bolts, and nails for joining components, offering reversibility and simplicity in assembly processes. |
Finishing Touches in Sheet Metal Fabrication
The finishing stage gives the fabricated part its final appearance and protective qualities. This phase can include a variety of processes, each designed to enhance the visual appeal, surface smoothness, and corrosion resistance of the metal. Finishing also plays a crucial role in preparing the product for its end-use environment, whether it’s an industrial setting, outdoor exposure, or consumer use.
- Sandblasting for Smooth Surfaces: Prepares the metal surface by removing imperfections, providing a smooth finish.
- Painting and Coating for Protection: Applies protective and decorative coatings, offering aesthetic appeal and resistance to corrosion and wear.
Cost-Effective Sheet Metal Fabrication
It is about maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste in terms of material and time. It starts with the choice of materials – selecting the correct type of metal that balances cost with performance. Advanced planning using CAD software helps in optimizing the design for minimal waste. Additionally, choosing the appropriate fabrication technique. Automation in processes like bending and welding can also reduce labor costs.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of sheet metal fabrication depends heavily on process optimization. It includes the efficient use of resources and streamlining workflow. Implementing lean manufacturing principles can reduce unnecessary steps and waste, leading to more economical production.
