Introduction
The electronic ignition system in a gas furnace is a modern development that offers more reliable performance than a standing pilot and offers energy savings through improved furnace efficiency. There are two basic types of electronic ignition systems:
intermittent pilot
An intermittent pilot system uses an electronically controlled high voltage electrical spark to turn on a pilot light and subsequently the main burners when the thermostat requires heat.
Hot surface ignition
A hot surface ignition system uses an electronically controlled resistance heating element, not unlike a lamp filament, to ignite the gas burner. If you are facing any kind of trouble regarding your furnace contact us at shortey’s Plumbing & Heating System. Our professional furnace repair technicians may help you. Understanding some of the basic components of a modern furnace will help you identify the type of furnace you have and narrow the list of possible problems. Here is a quick overview of the furnace designs and components found in high-efficiency furnaces using electronic ignition.
Types of Electronic Ignition Furnaces
A high-efficiency condensing furnace uses a plastic tube for ventilation and combustion air.
Most furnaces with electronic ignition are conventional or injection-induced furnaces or high-efficiency condensing furnaces.
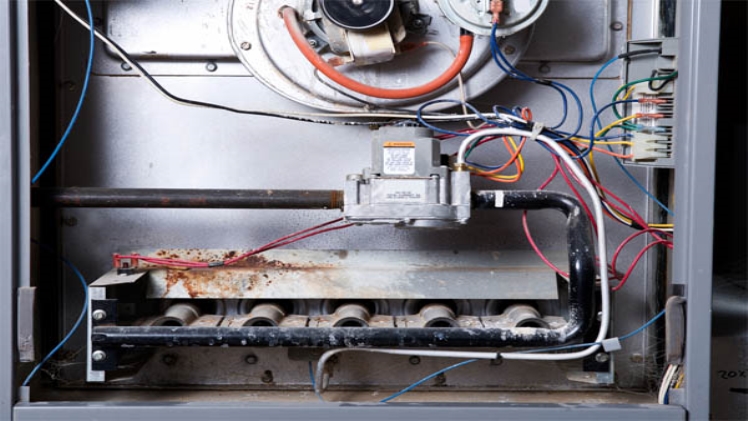
Induced draft furnaces use an intermittent pilot (IP) or hot surface ignition (HSI) instead of a standing pilot light. In addition, unlike a conventional furnace that creates a natural draft by drawing air out of an opening in front of the furnace, an induced draft furnace uses a small fan to drag the flue gases into the chimney. The combination of electronic ignition, electronic controls, and artificially created draft improves the efficiency of draft-induced furnaces over older conventional models. Condensing furnaces use two heat exchangers, where conventional furnaces use only one. After the gas is burned to heat the primary heat exchanger, the secondary heat exchanger draws heat from the hot exhaust gases, cooling them to the point where the water vapor in the exhaust condenses into water. The resulting flue gases are so cold that they can be expelled out through a plastic pipe (PVC), while the condensed water is directed to a drain in the floor. Condensing furnaces use hot surface ignition.
Troubleshooting an intermittent pilot (IP)
Normally found in induced draft furnaces, an intermittent pilot ignites the burner gas with a high voltage spark only when the thermostat calls for heat. Once the pilot is lit and the main burner detects the pilot flame (using a flame detection rod), the main burner ignites. The intermittent pilot flame goes out after the heating cycle and remains off until the next time the thermostat calls for heat.
The furnace gas valve for this type of furnace is identifiable with its solenoid designations: MV, PV, and PV / MV – where MV = main valve, PV = pilot valve, and PV / MV = common.
Common problems with IP ignition
Common problems with IP ignition include:
- Ignition does not, and the furnace will not continue.
- A spark is present, but the pilot does not light.
- Pilot lights, but the main burner does not light.
- Burners light up but turn off after a few seconds.