Anything preventing your blood from clotting or moving normally might trigger the formation of blood clots in your blood vessels. Unfortunately, blood clots in your deep veins might lead to serious vein issues, some of which could be fatal. A pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening DVT complication you are likely to have when the clot breaks and moves to your lungs. Are you suspecting your vein issue is more than it seems? If you are, Vascular Vein Centers is the place to visit. The vein experts address various vascular problems including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in East Orlando.
Is superficial venous thrombosis similar to deep vein thrombosis?
No! The two conditions are different vein complications that you should not ignore. A superficial venous thrombosis, also referred to as phlebitis, occurs when the clot develops in veins close to your skin’s surface. However, these clots might not disintegrate and travel to your lungs unless they shift from your superficial system straight to the deep venous system.
What symptoms are you likely to have with DVT?
The venous condition usually forms in either of your limbs (usually your legs). Not every deep vein thrombosis patient showcases symptoms. However, when they happen, you might have:
- Sudden swelling in the affected arm or leg
- Pain in your leg, especially when you stand
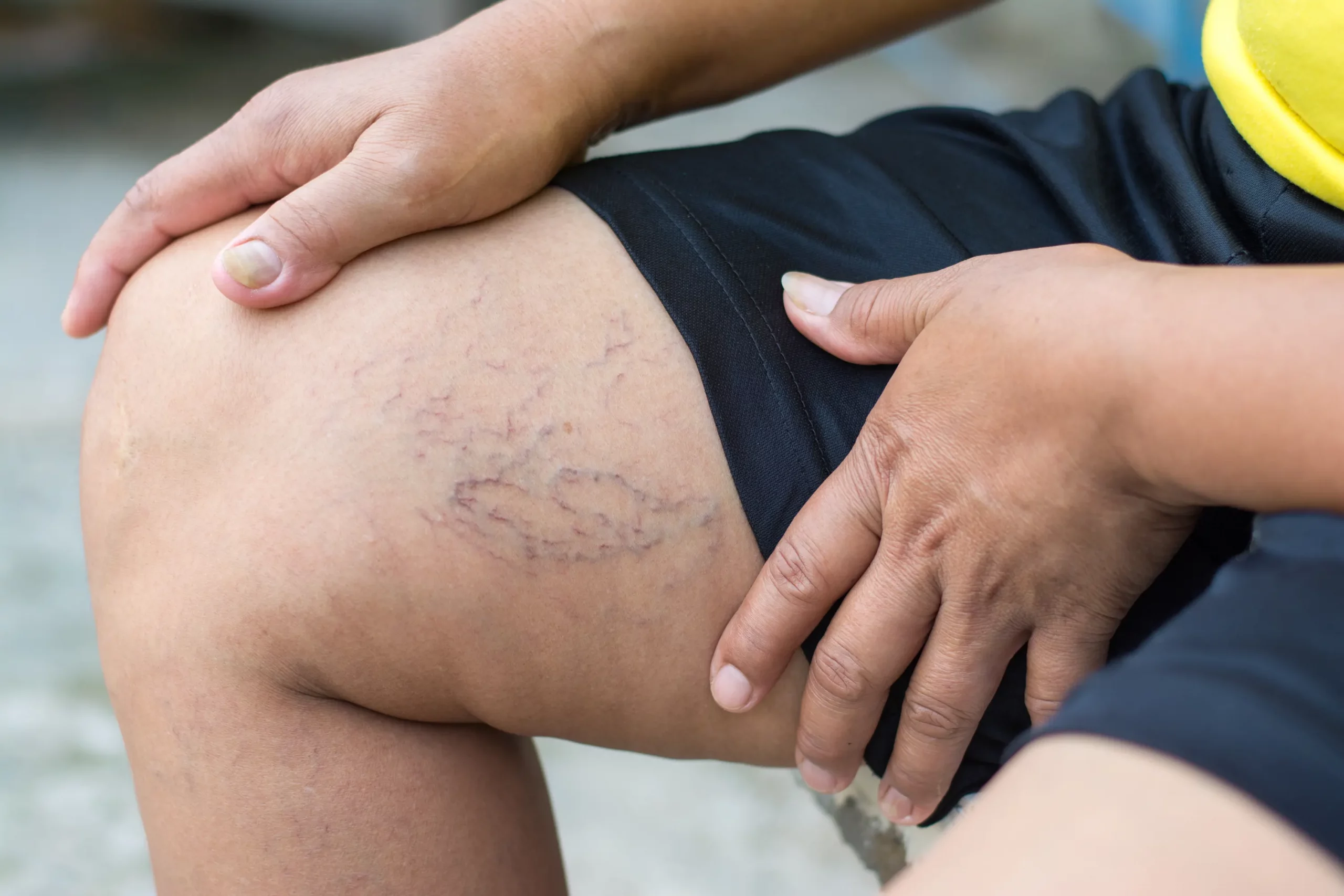
- The swollen part of your leg or arm might feel warmer than usual
- Discolored or red skin
- The blood vessels near your skin surface may appear larger than usual
Your healthcare provider will suspect the blood clot has moved to your lungs when you start having the following signs:
- Cough that might sometimes be bloody
- Rapid heartbeat
- Feeling dizzy
- Fast breathing or shortness of breath
- Sharp chest pains
- Unusual sweating
- Sharp back pain
How can you manage DVT?
DVT can make it challenging for you to move around. Your doctor might advise you to lie in bed or elevate your legs to enhance circulation and minimize swelling. Additionally, the medical professional might recommend the following steps:
- Standing up and walking for some minutes every hour (especially when you are awake)
- Wearing compression stockings
- Avoid physical activities likely to cause severe injuries
- Avoid tight-fitting attires that might minimize circulation in your legs
- Exercise your leg muscles regularly, mainly if your work entails sitting for extensive hours
There are several ways your healthcare provider might help you manage DVT. Besides medications and wearing compression socks, your primary physician might suggest a more intensive option if the clot is extensive.
Can you prevent DVT?
Minimizing your chances of developing DVT is possible. Your physical therapist might advise you to:
- Manage your weight. Obesity increases your risk of developing DVT. Exercises might help lower your risk of having blood clots. Physical activities are crucial, especially if you sit or travel a lot.
- Do not sit still for long. Extended bed rest after sickness or a surgical procedure is risky as it might prompt the development of blood clots. If possible, try walking around or exercising your lower legs.
- Stop unhealthy habits like smoking as they might increase your chances of developing DVT
Contact a vein expert for more inquiries on DVT.